注意
转到末尾下载完整的示例代码。
轴刻度#
默认情况下,Matplotlib 使用线性刻度在轴上显示数据。Matplotlib 也支持对数刻度以及其他不常见的刻度。通常这可以通过直接使用 set_xscale 或 set_yscale 方法来完成。
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.scale as mscale
from matplotlib.ticker import FixedLocator, NullFormatter
fig, axs = plt.subplot_mosaic([['linear', 'linear-log'],
['log-linear', 'log-log']], layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(0, 3*np.pi, 0.1)
y = 2 * np.sin(x) + 3
ax = axs['linear']
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('linear')
ax.set_ylabel('linear')
ax = axs['linear-log']
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('linear')
ax.set_ylabel('log')
ax = axs['log-linear']
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('log')
ax.set_ylabel('linear')
ax = axs['log-log']
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xscale('log')
ax.set_yscale('log')
ax.set_xlabel('log')
ax.set_ylabel('log')
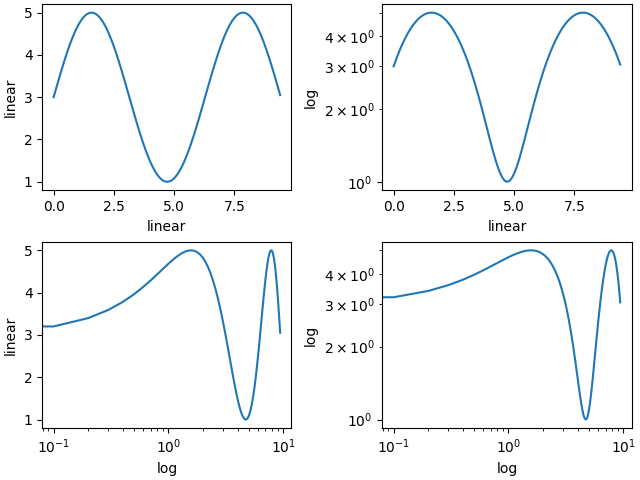
loglog 和 semilogx/y#
对数轴使用非常频繁,因此有一组执行相同操作的辅助函数:semilogy、semilogx 和 loglog。
fig, axs = plt.subplot_mosaic([['linear', 'linear-log'],
['log-linear', 'log-log']], layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(0, 3*np.pi, 0.1)
y = 2 * np.sin(x) + 3
ax = axs['linear']
ax.plot(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('linear')
ax.set_ylabel('linear')
ax.set_title('plot(x, y)')
ax = axs['linear-log']
ax.semilogy(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('linear')
ax.set_ylabel('log')
ax.set_title('semilogy(x, y)')
ax = axs['log-linear']
ax.semilogx(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('log')
ax.set_ylabel('linear')
ax.set_title('semilogx(x, y)')
ax = axs['log-log']
ax.loglog(x, y)
ax.set_xlabel('log')
ax.set_ylabel('log')
ax.set_title('loglog(x, y)')
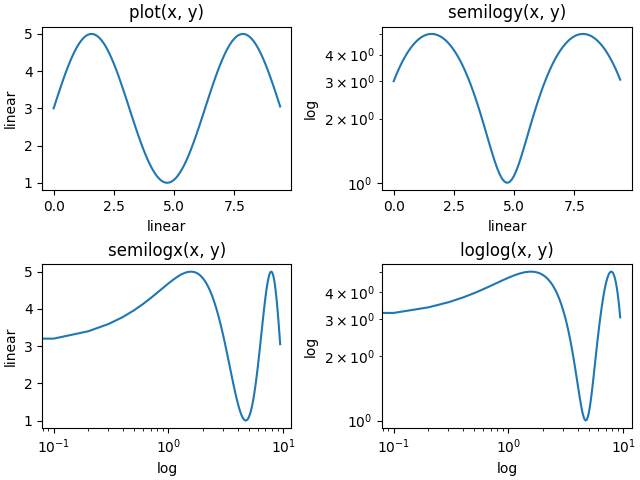
其他内置刻度#
还有其他可用的刻度。已注册刻度的列表可以从 scale.get_scale_names 返回。
print(mscale.get_scale_names())
['asinh', 'function', 'functionlog', 'linear', 'log', 'logit', 'symlog']
fig, axs = plt.subplot_mosaic([['asinh', 'symlog'],
['log', 'logit']], layout='constrained')
x = np.arange(0, 1000)
for name, ax in axs.items():
if name in ['asinh', 'symlog']:
yy = x - np.mean(x)
elif name in ['logit']:
yy = (x-np.min(x))
yy = yy / np.max(np.abs(yy))
else:
yy = x
ax.plot(yy, yy)
ax.set_yscale(name)
ax.set_title(name)
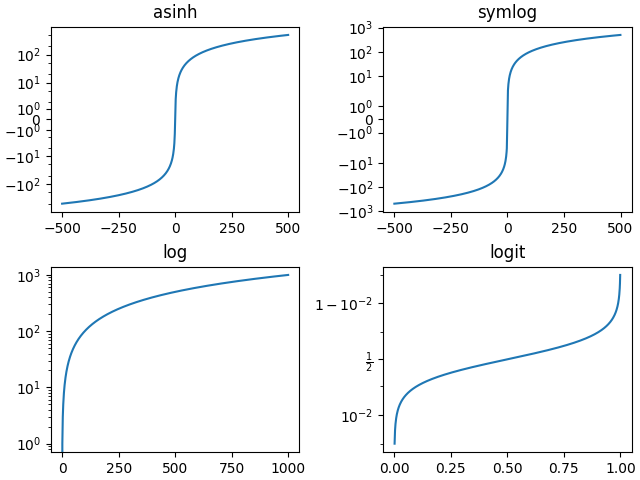
刻度的可选参数#
一些默认刻度具有可选参数。这些参数在 scale 中各自刻度的 API 参考文档中有说明。可以更改绘图对数的底(例如下面的 2)或 `'symlog'` 的线性阈值范围。
fig, axs = plt.subplot_mosaic([['log', 'symlog']], layout='constrained',
figsize=(6.4, 3))
for name, ax in axs.items():
if name in ['log']:
ax.plot(x, x)
ax.set_yscale('log', base=2)
ax.set_title('log base=2')
else:
ax.plot(x - np.mean(x), x - np.mean(x))
ax.set_yscale('symlog', linthresh=100)
ax.set_title('symlog linthresh=100')
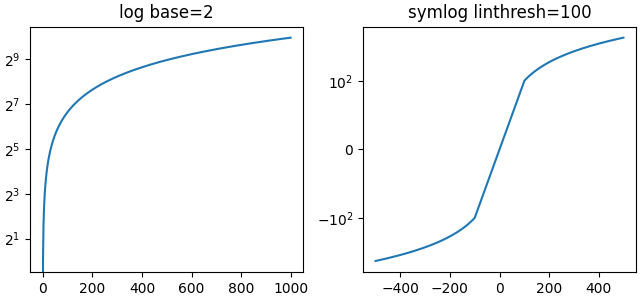
任意函数刻度#
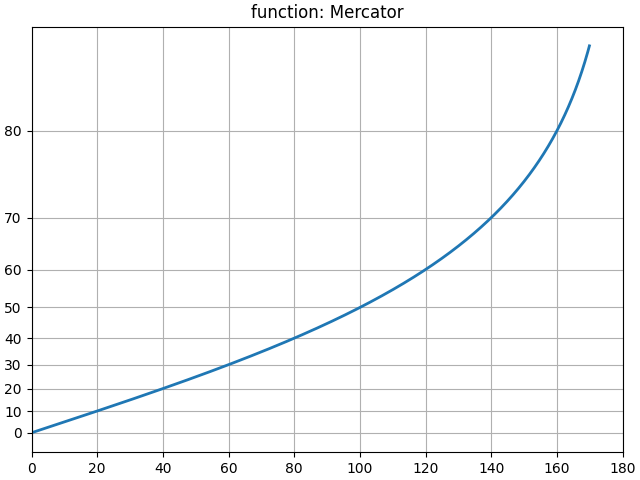
用户可以定义一个完整的刻度类并将其传递给 set_xscale 和 set_yscale(参见 自定义刻度)。一个捷径是使用“函数”刻度,并传入 forward 和 inverse 函数作为额外参数。以下示例对 y 轴执行 墨卡托变换。
# Function Mercator transform
def forward(a):
a = np.deg2rad(a)
return np.rad2deg(np.log(np.abs(np.tan(a) + 1.0 / np.cos(a))))
def inverse(a):
a = np.deg2rad(a)
return np.rad2deg(np.arctan(np.sinh(a)))
t = np.arange(0, 170.0, 0.1)
s = t / 2.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained')
ax.plot(t, s, '-', lw=2)
ax.set_yscale('function', functions=(forward, inverse))
ax.set_title('function: Mercator')
ax.grid(True)
ax.set_xlim([0, 180])
ax.yaxis.set_minor_formatter(NullFormatter())
ax.yaxis.set_major_locator(FixedLocator(np.arange(0, 90, 10)))
什么是“刻度”?#
刻度是附加到轴上的对象。类文档位于 scale。 set_xscale 和 set_yscale 在各自的 Axis 对象上设置刻度。可以使用 get_scale 确定轴上的刻度。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(layout='constrained',
figsize=(3.2, 3))
ax.semilogy(x, x)
print(ax.xaxis.get_scale())
print(ax.yaxis.get_scale())
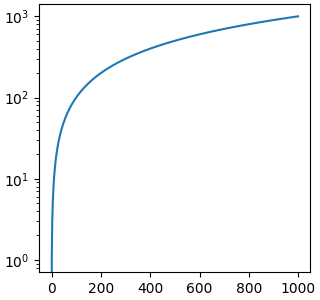
linear
log
设置刻度有三个作用。首先,它定义了轴上的一个变换,该变换将数据值映射到沿轴的位置。此变换可以通过 get_transform 访问。
print(ax.yaxis.get_transform())
LogTransform(base=10, nonpositive='clip')
轴上的变换是一个相对底层的概念,但它是 set_scale 所扮演的重要角色之一。
设置刻度还会设置适合该刻度的默认刻度定位器(ticker)和刻度格式化器。具有“对数”刻度的轴拥有一个 LogLocator 以在十年间隔处选择刻度,以及一个 LogFormatter 以在十年上使用科学记数法。
print('X axis')
print(ax.xaxis.get_major_locator())
print(ax.xaxis.get_major_formatter())
print('Y axis')
print(ax.yaxis.get_major_locator())
print(ax.yaxis.get_major_formatter())
X axis
<matplotlib.ticker.AutoLocator object at 0x7315fb20d370>
<matplotlib.ticker.ScalarFormatter object at 0x7315fbfcd5a0>
Y axis
<matplotlib.ticker.LogLocator object at 0x7315faf8f250>
<matplotlib.ticker.LogFormatterSciNotation object at 0x7315fb1e6cd0>
脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 8.415 秒)