注意
转到末尾下载完整的示例代码。
注解#
注解是图形元素,通常是文本片段,用于解释、添加上下文或以其他方式突出显示可视化数据的某些部分。annotate支持多种坐标系,可灵活定位数据和注解之间的相对位置,以及多种文本样式选项。Axes.annotate 还提供从文本到数据的可选箭头,此箭头可以通过各种方式进行样式设置。text也可用于简单的文本注解,但其定位和样式灵活性不如annotate。
基本注解#
在注解中,有两个点需要考虑:被注解数据的位置 xy 和注解文本的位置 xytext。这两个参数都是 (x, y) 元组。
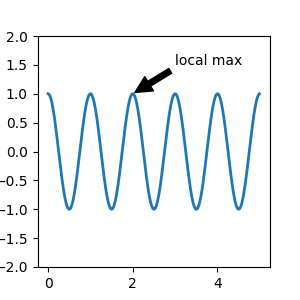
在此示例中,xy(箭头尖端)和 xytext(文本位置)都在数据坐标中。您可以选择多种其他坐标系——可以使用以下字符串之一为 xycoords 和 textcoords 指定 xy 和 xytext 的坐标系(默认为 'data')
参数 |
坐标系 |
|---|---|
'figure points' |
距离图形左下角的点 |
'figure pixels' |
距离图形左下角的像素 |
'figure fraction' |
(0, 0) 是图形的左下角,(1, 1) 是右上角 |
'axes points' |
距离 Axes 左下角的点 |
'axes pixels' |
距离 Axes 左下角的像素 |
'axes fraction' |
(0, 0) 是 Axes 的左下角,(1, 1) 是右上角 |
'data' |
使用 Axes 数据坐标系 |
以下字符串也适用于 textcoords 参数
参数 |
坐标系 |
|---|---|
'offset points' |
距 xy 值的偏移量(点) |
'offset pixels' |
距 xy 值的偏移量(像素) |
对于物理坐标系(点或像素),原点是图形或 Axes 的左下角。点是印刷点,这意味着它们是一个物理单位,测量值为 1/72 英寸。点和像素在物理坐标绘图中有更详细的讨论。
注解数据#
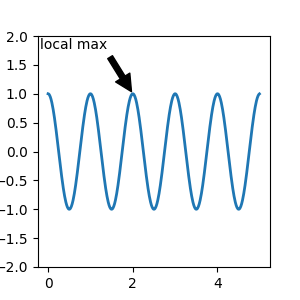
此示例将文本坐标放置在分数 Axes 坐标中
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
t = np.arange(0.0, 5.0, 0.01)
s = np.cos(2*np.pi*t)
line, = ax.plot(t, s, lw=2)
ax.annotate('local max', xy=(2, 1), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.01, .99), textcoords='axes fraction',
va='top', ha='left',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05))
ax.set_ylim(-2, 2)
注解 Artist#
注解可以通过将 Artist 作为 xycoords 传入来相对于 Artist 实例进行定位。然后 xy 被解释为 Artist 边界框的分数。
import matplotlib.patches as mpatches
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
arr = mpatches.FancyArrowPatch((1.25, 1.5), (1.75, 1.5),
arrowstyle='->,head_width=.15', mutation_scale=20)
ax.add_patch(arr)
ax.annotate("label", (.5, .5), xycoords=arr, ha='center', va='bottom')
ax.set(xlim=(1, 2), ylim=(1, 2))
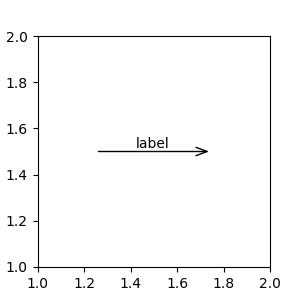
此处,注解相对于箭头的左下角放置在 (.5,.5) 位置,并在此位置垂直和水平对齐。垂直方向上,底部与该参考点对齐,以便标签位于线上方。有关链接注解 Artist 的示例,请参阅注解的坐标系的Artist 部分。
带箭头的注解#
您可以通过在可选关键字参数 arrowprops 中提供一个箭头属性字典来启用从文本到注解点的箭头绘制。
arrowprops 键 |
描述 |
|---|---|
width |
箭头的宽度(以点为单位) |
frac |
箭头长度中箭头头部所占的比例 |
headwidth |
箭头头部底部的宽度(以点为单位) |
shrink |
将箭头尖端和底部从注解点和文本处向外移动百分比 |
**kwargs |
|
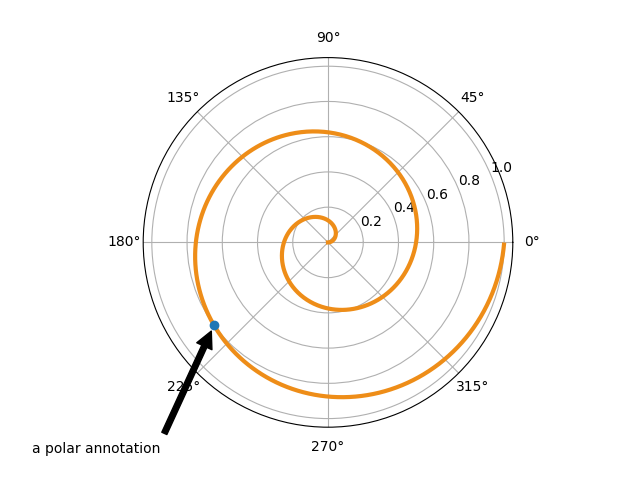
在下面的示例中,xy 点在数据坐标系中,因为 xycoords 默认为 'data'。对于极坐标 Axes,这位于(theta,radius)空间中。此示例中的文本放置在分数图形坐标系中。matplotlib.text.Text 关键字参数,如 horizontalalignment、verticalalignment 和 fontsize,从annotate传递给Text实例。
fig = plt.figure()
ax = fig.add_subplot(projection='polar')
r = np.arange(0, 1, 0.001)
theta = 2 * 2*np.pi * r
line, = ax.plot(theta, r, color='#ee8d18', lw=3)
ind = 800
thisr, thistheta = r[ind], theta[ind]
ax.plot([thistheta], [thisr], 'o')
ax.annotate('a polar annotation',
xy=(thistheta, thisr), # theta, radius
xytext=(0.05, 0.05), # fraction, fraction
textcoords='figure fraction',
arrowprops=dict(facecolor='black', shrink=0.05),
horizontalalignment='left',
verticalalignment='bottom')
有关使用箭头绘图的更多信息,请参阅自定义注解箭头
将文本注解相对于数据放置#
通过将 textcoords 关键字参数设置为 'offset points' 或 'offset pixels',可以将注解放置在相对于注解的 xy 输入的偏移量处。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
x = [1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
y = [2, 4, 6, 8, 10]
annotations = ["A", "B", "C", "D", "E"]
ax.scatter(x, y, s=20)
for xi, yi, text in zip(x, y, annotations):
ax.annotate(text,
xy=(xi, yi), xycoords='data',
xytext=(1.5, 1.5), textcoords='offset points')
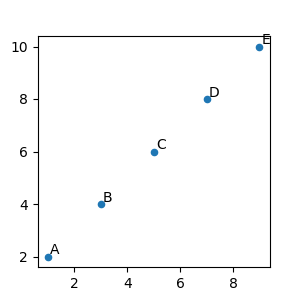
注解相对于 xy 值偏移 1.5 个点(1.5*1/72 英寸)。
高级注解#
我们建议在阅读本节之前阅读基本注解、text()和annotate()。
带框文本的注解#
text 接受 bbox 关键字参数,该参数在文本周围绘制一个框。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(5, 5))
t = ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Direction",
ha="center", va="center", rotation=45, size=15,
bbox=dict(boxstyle="rarrow,pad=0.3",
fc="lightblue", ec="steelblue", lw=2))
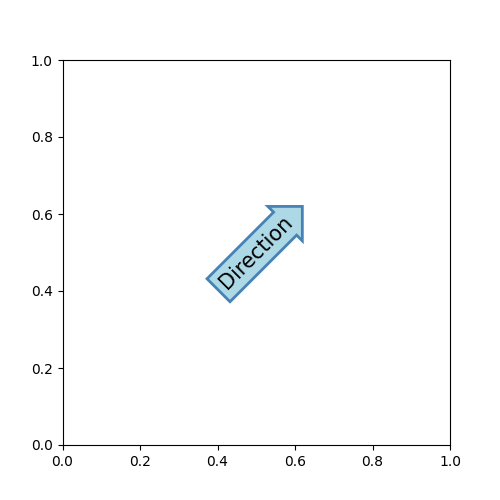
参数是框样式的名称及其属性作为关键字参数。目前,以下框样式已实现:
类 |
名称 |
属性 |
|---|---|---|
Circle |
|
pad=0.3 |
DArrow |
|
pad=0.3 |
Ellipse |
|
pad=0.3 |
LArrow |
|
pad=0.3 |
RArrow |
|
pad=0.3 |
Round |
|
pad=0.3,rounding_size=None |
Round4 |
|
pad=0.3,rounding_size=None |
Roundtooth |
|
pad=0.3,tooth_size=None |
Sawtooth |
|
pad=0.3,tooth_size=None |
Square |
|
pad=0.3 |

与文本关联的补丁对象(框)可以通过以下方式访问:
bb = t.get_bbox_patch()
返回值是一个FancyBboxPatch;补丁属性(facecolor、edgewidth 等)可以像往常一样访问和修改。FancyBboxPatch.set_boxstyle 设置框的形状。
bb.set_boxstyle("rarrow", pad=0.6)
属性参数也可以在样式名称中用逗号分隔指定。
bb.set_boxstyle("rarrow, pad=0.6")
定义自定义框样式#
自定义框样式可以作为函数实现,该函数接受指定矩形框和“变异”量的参数,并返回“变异”路径。具体签名如下所示 custom_box_style。
在这里,我们返回一个新路径,它在框的左侧添加一个“箭头”形状。
然后,可以通过将 bbox=dict(boxstyle=custom_box_style, ...) 传递给 Axes.text 来使用自定义框样式。
from matplotlib.path import Path
def custom_box_style(x0, y0, width, height, mutation_size):
"""
Given the location and size of the box, return the path of the box around it.
Rotation is automatically taken care of.
Parameters
----------
x0, y0, width, height : float
Box location and size.
mutation_size : float
Mutation reference scale, typically the text font size.
"""
# padding
mypad = 0.3
pad = mutation_size * mypad
# width and height with padding added.
width = width + 2 * pad
height = height + 2 * pad
# boundary of the padded box
x0, y0 = x0 - pad, y0 - pad
x1, y1 = x0 + width, y0 + height
# return the new path
return Path([(x0, y0), (x1, y0), (x1, y1), (x0, y1),
(x0-pad, (y0+y1)/2), (x0, y0), (x0, y0)],
closed=True)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Test", size=30, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30,
bbox=dict(boxstyle=custom_box_style, alpha=0.2))
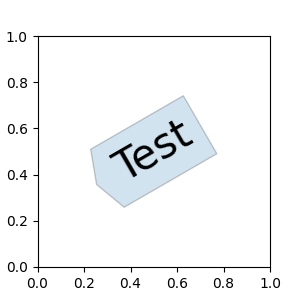
同样,自定义框样式可以作为实现 __call__ 的类实现。
然后可以将这些类注册到 BoxStyle._style_list 字典中,从而允许将框样式指定为字符串,bbox=dict(boxstyle="registered_name,param=value,...", ...)。请注意,此注册依赖于内部 API,因此未正式支持。
from matplotlib.patches import BoxStyle
class MyStyle:
"""A simple box."""
def __init__(self, pad=0.3):
"""
The arguments must be floats and have default values.
Parameters
----------
pad : float
amount of padding
"""
self.pad = pad
super().__init__()
def __call__(self, x0, y0, width, height, mutation_size):
"""
Given the location and size of the box, return the path of the box around it.
Rotation is automatically taken care of.
Parameters
----------
x0, y0, width, height : float
Box location and size.
mutation_size : float
Reference scale for the mutation, typically the text font size.
"""
# padding
pad = mutation_size * self.pad
# width and height with padding added
width = width + 2 * pad
height = height + 2 * pad
# boundary of the padded box
x0, y0 = x0 - pad, y0 - pad
x1, y1 = x0 + width, y0 + height
# return the new path
return Path([(x0, y0), (x1, y0), (x1, y1), (x0, y1),
(x0-pad, (y0+y1)/2), (x0, y0), (x0, y0)],
closed=True)
BoxStyle._style_list["angled"] = MyStyle # Register the custom style.
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.text(0.5, 0.5, "Test", size=30, va="center", ha="center", rotation=30,
bbox=dict(boxstyle="angled,pad=0.5", alpha=0.2))
del BoxStyle._style_list["angled"] # Unregister it.
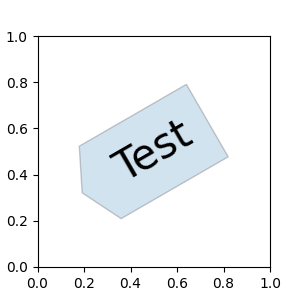
类似地,您可以定义自定义的 ConnectionStyle 和自定义的 ArrowStyle。查看 patches 中的源代码以了解每个类的定义方式。
自定义注解箭头#
通过指定 arrowprops 参数,可以选择绘制连接 xy 到 xytext 的箭头。要仅绘制箭头,请将空字符串作为第一个参数。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.annotate("",
xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.8, 0.8), textcoords='data',
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->", connectionstyle="arc3"))
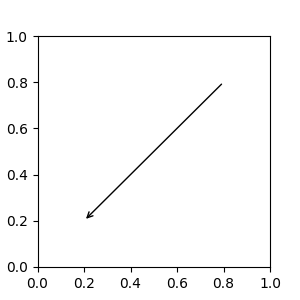
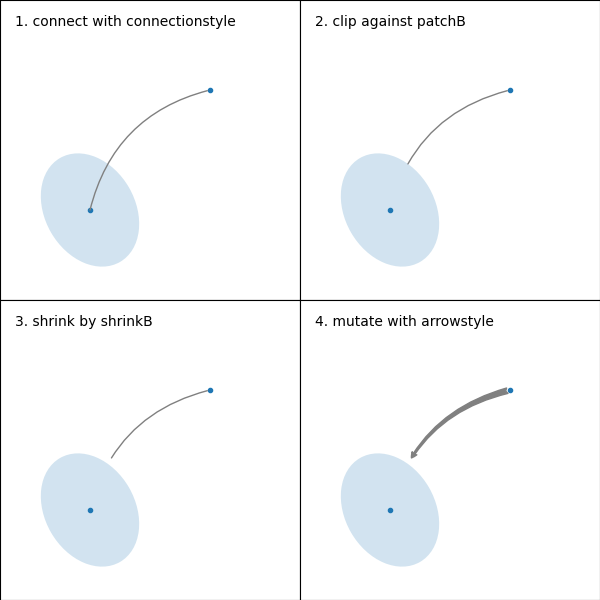
箭头的绘制方式如下:
根据 connectionstyle 参数的指定,创建连接两点的路径。
如果设置了 patchA 和 patchB,则路径会被裁剪以避开这些补丁。
路径会进一步由 shrinkA 和 shrinkB(以像素为单位)缩小。
根据 arrowstyle 参数的指定,路径被转换为箭头补丁。
两点之间连接路径的创建由 connectionstyle 键控制,以下样式可用:
名称 |
属性 |
|---|---|
|
angleA=90,angleB=0,rad=0.0 |
|
angleA=90,angleB=0 |
|
angleA=0,angleB=0,armA=None,armB=None,rad=0.0 |
|
rad=0.0 |
|
armA=0.0,armB=0.0,fraction=0.3,angle=None |
请注意,angle3 和 arc3 中的“3”表示结果路径是二次样条段(三个控制点)。如下所述,某些箭头样式选项只能在连接路径为二次样条时使用。
下面示例(有限地)演示了每种连接样式的行为。(警告:bar 样式的行为目前尚未明确定义,未来可能会更改)。
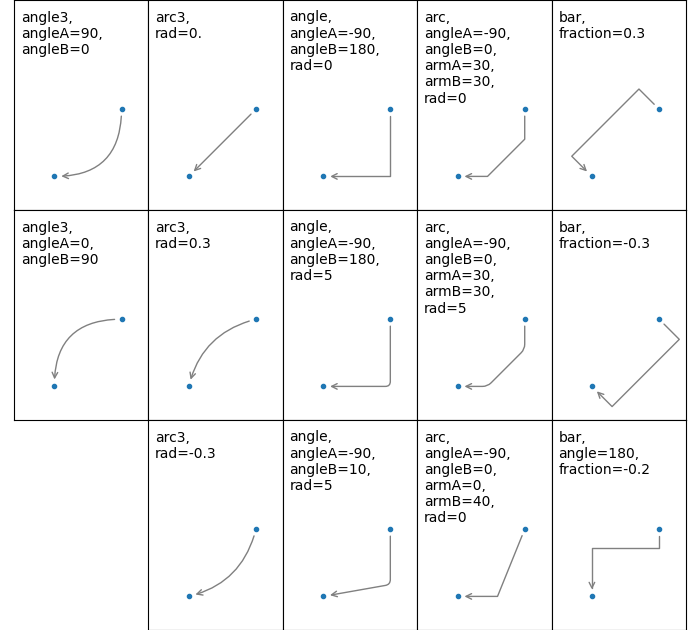
注解的连接样式
连接路径(裁剪和缩小后)然后根据给定的 arrowstyle 转换为箭头补丁。
名称 |
属性 |
|---|---|
|
None |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
|
widthB=1.0,lengthB=0.2,angleB=None |
|
widthA=1.0,widthB=1.0 |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.2 |
|
head_length=0.4,head_width=0.4,tail_width=0.4 |
|
head_length=0.5,head_width=0.5,tail_width=0.2 |
|
tail_width=0.3,shrink_factor=0.5 |

某些箭头样式仅适用于生成二次样条段的连接样式。它们是 fancy、simple 和 wedge。对于这些箭头样式,您必须使用“angle3”或“arc3”连接样式。
如果给定注解字符串,则补丁默认为文本的 bbox 补丁。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.annotate("Test",
xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.8, 0.8), textcoords='data',
size=20, va="center", ha="center",
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="simple",
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=-0.2"))
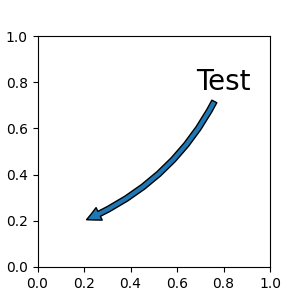
与 text 一样,可以使用 bbox 参数在文本周围绘制一个框。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ann = ax.annotate("Test",
xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.8, 0.8), textcoords='data',
size=20, va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="w"),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="-|>",
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=-0.2",
fc="w"))
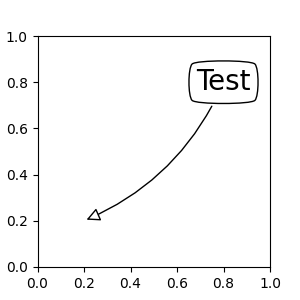
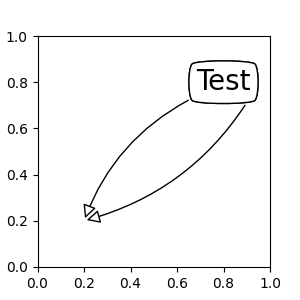
默认情况下,起始点设置为文本范围的中心。这可以通过 relpos 键值进行调整。这些值被标准化为文本的范围。例如,(0, 0) 表示左下角,(1, 1) 表示右上角。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ann = ax.annotate("Test",
xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.8, 0.8), textcoords='data',
size=20, va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="w"),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="-|>",
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=0.2",
relpos=(0., 0.),
fc="w"))
ann = ax.annotate("Test",
xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords='data',
xytext=(0.8, 0.8), textcoords='data',
size=20, va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round4", fc="w"),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="-|>",
connectionstyle="arc3,rad=-0.2",
relpos=(1., 0.),
fc="w"))
将 Artist 放置在固定 Axes 位置#
有一些 Artist 类可以放置在 Axes 中的固定位置。一个常见的例子是图例。这种类型的 Artist 可以通过使用 OffsetBox 类创建。一些预定义的类在 matplotlib.offsetbox 和 mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.anchored_artists 中可用。
from matplotlib.offsetbox import AnchoredText
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
at = AnchoredText("Figure 1a",
prop=dict(size=15), frameon=True, loc='upper left')
at.patch.set_boxstyle("round,pad=0.,rounding_size=0.2")
ax.add_artist(at)
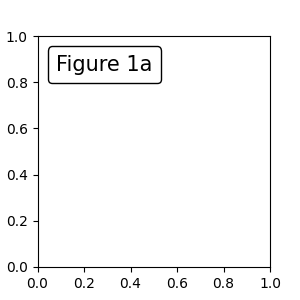
loc 关键字与图例命令中的含义相同。
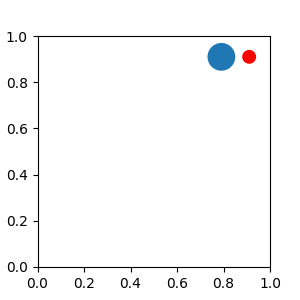
一个简单的应用是,在创建时,Artist(或 Artist 集合)的大小以像素为单位已知。例如,如果您想绘制一个固定大小为 20 像素 x 20 像素(半径 = 10 像素)的圆形,您可以使用 AnchoredDrawingArea。实例以绘图区域的大小(以像素为单位)创建,并且可以将任意 Artist 添加到绘图区域。请注意,添加到绘图区域的 Artist 的范围与绘图区域本身的放置无关。只有初始大小才重要。
添加到绘图区域的 Artist 不应设置变换(它将被覆盖),并且这些 Artist 的尺寸被解释为像素坐标,即,上述示例中圆的半径分别为 10 像素和 5 像素。
from matplotlib.patches import Circle
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.anchored_artists import AnchoredDrawingArea
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ada = AnchoredDrawingArea(40, 20, 0, 0,
loc='upper right', pad=0., frameon=False)
p1 = Circle((10, 10), 10)
ada.drawing_area.add_artist(p1)
p2 = Circle((30, 10), 5, fc="r")
ada.drawing_area.add_artist(p2)
ax.add_artist(ada)
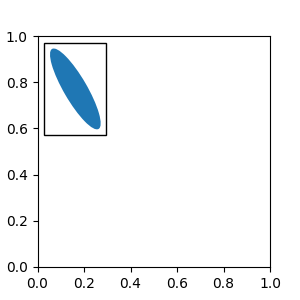
有时,您希望您的 Artist 随数据坐标(或画布像素以外的其他坐标)缩放。您可以使用 AnchoredAuxTransformBox 类。这类似于 AnchoredDrawingArea,不同之处在于 Artist 的范围是在绘图时根据指定变换确定的。
下面示例中的椭圆的宽度和高度将分别对应数据坐标中的 0.1 和 0.4,并且当 Axes 的视图限制更改时将自动缩放。
from matplotlib.patches import Ellipse
from mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.anchored_artists import AnchoredAuxTransformBox
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
box = AnchoredAuxTransformBox(ax.transData, loc='upper left')
el = Ellipse((0, 0), width=0.1, height=0.4, angle=30) # in data coordinates!
box.drawing_area.add_artist(el)
ax.add_artist(box)
另一种将 Artist 相对于父 Axes 或锚点进行锚定的方法是通过 AnchoredOffsetbox 的 bbox_to_anchor 参数。然后,可以使用 HPacker 和 VPacker 自动将此 Artist 定位到另一个 Artist。
from matplotlib.offsetbox import (AnchoredOffsetbox, DrawingArea, HPacker,
TextArea)
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
box1 = TextArea(" Test: ", textprops=dict(color="k"))
box2 = DrawingArea(60, 20, 0, 0)
el1 = Ellipse((10, 10), width=16, height=5, angle=30, fc="r")
el2 = Ellipse((30, 10), width=16, height=5, angle=170, fc="g")
el3 = Ellipse((50, 10), width=16, height=5, angle=230, fc="b")
box2.add_artist(el1)
box2.add_artist(el2)
box2.add_artist(el3)
box = HPacker(children=[box1, box2],
align="center",
pad=0, sep=5)
anchored_box = AnchoredOffsetbox(loc='lower left',
child=box, pad=0.,
frameon=True,
bbox_to_anchor=(0., 1.02),
bbox_transform=ax.transAxes,
borderpad=0.,)
ax.add_artist(anchored_box)
fig.subplots_adjust(top=0.8)
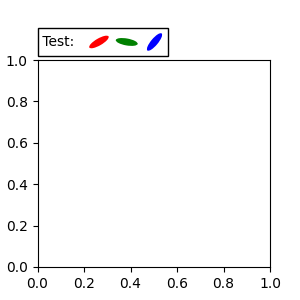
请注意,与 Legend 不同,bbox_transform 默认为 IdentityTransform。
注解的坐标系#
Matplotlib 注解支持多种类型的坐标系。基本注解中的示例使用了 data 坐标系;其他更高级的选项有:
Transform 实例#
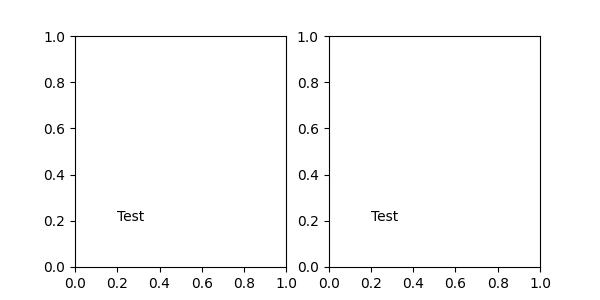
变换将坐标映射到不同的坐标系中,通常是显示坐标系。有关详细说明,请参阅变换教程。这里,变换对象用于标识相应点的坐标系。例如,Axes.transAxes 变换将注解相对于 Axes 坐标定位;因此使用它与将坐标系设置为“axes fraction”是相同的。
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(6, 3))
ax1.annotate("Test", xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords=ax1.transAxes)
ax2.annotate("Test", xy=(0.2, 0.2), xycoords="axes fraction")
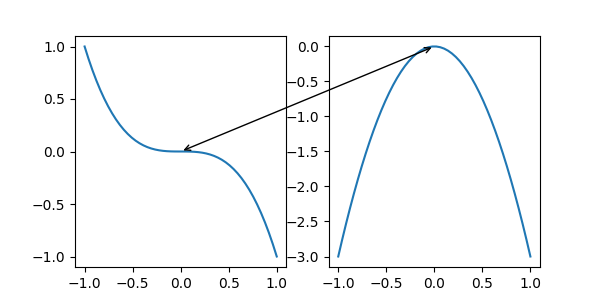
另一个常用的 Transform 实例是 Axes.transData。此变换是 Axes 中绘制数据的坐标系。在此示例中,它用于在两个 Axes 中的相关数据点之间绘制箭头。我们传递了一个空文本,因为在这种情况下,注解连接了数据点。
x = np.linspace(-1, 1)
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(6, 3))
ax1.plot(x, -x**3)
ax2.plot(x, -3*x**2)
ax2.annotate("",
xy=(0, 0), xycoords=ax1.transData,
xytext=(0, 0), textcoords=ax2.transData,
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="<->"))
Artist 实例#
xy 值(或 xytext)被解释为 Artist 边界框 (bbox) 的分数坐标。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(3, 3))
an1 = ax.annotate("Test 1",
xy=(0.5, 0.5), xycoords="data",
va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", fc="w"))
an2 = ax.annotate("Test 2",
xy=(1, 0.5), xycoords=an1, # (1, 0.5) of an1's bbox
xytext=(30, 0), textcoords="offset points",
va="center", ha="left",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", fc="w"),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
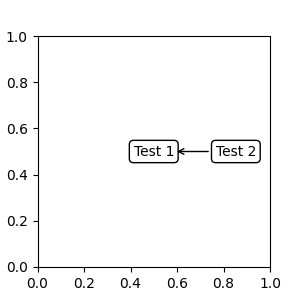
请注意,您必须确保坐标 Artist (本例中为 an1) 的范围在 an2 绘制之前确定。通常,这意味着 an2 需要在 an1 之后绘制。所有边界框的基类是 BboxBase。
可调用对象,返回 BboxBase 的 Transform#
一个可调用对象,它接受渲染器实例作为唯一参数,并返回一个 Transform 或一个 BboxBase。例如,Artist.get_window_extent 的返回值是一个 bbox,因此此方法与(2)传入 Artist 是相同的。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=1, figsize=(3, 3))
an1 = ax.annotate("Test 1",
xy=(0.5, 0.5), xycoords="data",
va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", fc="w"))
an2 = ax.annotate("Test 2",
xy=(1, 0.5), xycoords=an1.get_window_extent,
xytext=(30, 0), textcoords="offset points",
va="center", ha="left",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", fc="w"),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
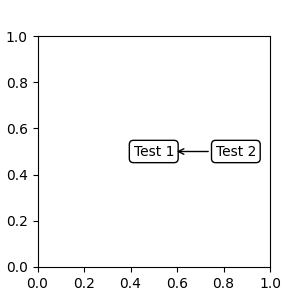
Artist.get_window_extent 是 Axes 对象的边界框,因此与将坐标系设置为 axes fraction 相同。
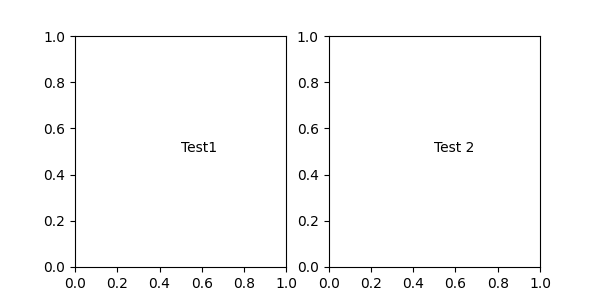
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(6, 3))
an1 = ax1.annotate("Test1", xy=(0.5, 0.5), xycoords="axes fraction")
an2 = ax2.annotate("Test 2", xy=(0.5, 0.5), xycoords=ax2.get_window_extent)
混合坐标规范#
一对混合坐标规范——第一个用于 x 坐标,第二个用于 y 坐标。例如,x=0.5 在数据坐标中,y=1 在归一化 Axes 坐标中。
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
ax.annotate("Test", xy=(0.5, 1), xycoords=("data", "axes fraction"))
ax.axvline(x=.5, color='lightgray')
ax.set(xlim=(0, 2), ylim=(1, 2))
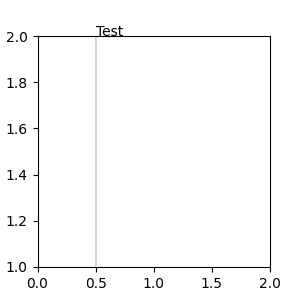
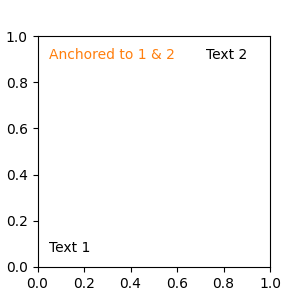
任何支持的坐标系都可以在混合规范中使用。例如,文本“Anchored to 1 & 2”是相对于两个 Text Artist 定位的。
text.OffsetFrom#
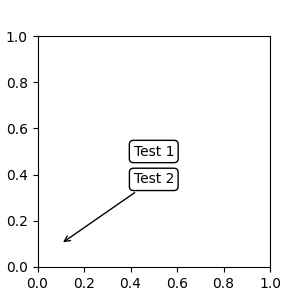
有时,您希望您的注解具有一些“偏移点”,但不是从注解点,而是从其他点或 Artist。在这种情况下,text.OffsetFrom 是一个有用的帮助工具。
from matplotlib.text import OffsetFrom
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(3, 3))
an1 = ax.annotate("Test 1", xy=(0.5, 0.5), xycoords="data",
va="center", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", fc="w"))
offset_from = OffsetFrom(an1, (0.5, 0))
an2 = ax.annotate("Test 2", xy=(0.1, 0.1), xycoords="data",
xytext=(0, -10), textcoords=offset_from,
# xytext is offset points from "xy=(0.5, 0), xycoords=an1"
va="top", ha="center",
bbox=dict(boxstyle="round", fc="w"),
arrowprops=dict(arrowstyle="->"))
非文本注解#
使用 ConnectionPatch#
ConnectionPatch 就像一个没有文本的注解。虽然在大多数情况下 annotate 就足够了,但当您想要连接不同 Axes 中的点时,ConnectionPatch 会很有用。例如,在这里我们将 ax1 数据坐标中的点 xy 连接到 ax2 数据坐标中的点 xy。
from matplotlib.patches import ConnectionPatch
fig, (ax1, ax2) = plt.subplots(nrows=1, ncols=2, figsize=(6, 3))
xy = (0.3, 0.2)
con = ConnectionPatch(xyA=xy, coordsA=ax1.transData,
xyB=xy, coordsB=ax2.transData)
fig.add_artist(con)
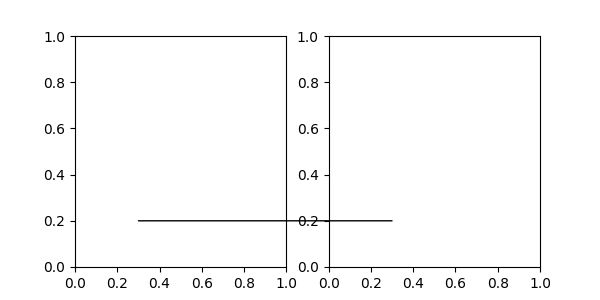
在这里,我们将 ConnectionPatch 添加到 figure(使用 add_artist),而不是添加到任何一个 Axes。这确保了 ConnectionPatch Artist 绘制在两个 Axes 之上,并且在使用 constrained_layout 进行 Axes 定位时也是必要的。
Axes 之间的缩放效果#
mpl_toolkits.axes_grid1.inset_locator 定义了一些用于连接两个 Axes 的补丁类。

脚本总运行时间: (0 分钟 4.013 秒)